LH Levels: Understanding Normal Ranges and The Benefit of Testing
Why do we need to check our LH levels? Many women naturally maintain LH within a normal range, yet some encounter difficulties with levels that are either too high or too low, posing challenges for those attempting to conceive. Luteinizing hormone (LH) is key in regulating the menstrual cycle and supporting reproductive functions in women, including ovulation and preparation for pregnancy.
If you’re considering pregnancy or having trouble conceiving, testing your LH levels can be useful. Such testing can help pinpoint your fertile window and reveal if there are any concerns with your LH levels being outside the normal range.

Key Takeaways
- LH is a significant cycling hormone primarily involved in properly regulating women’s menstrual cycle and helping trigger ovulation.
- Several different lifestyle factors cause high LH levels, it (high level LH) can be associated with PCOS.
- On the other hand, low LH levels are mainly caused by stress and an unhealthy diet. Levels are low in people who have various pituitary gland problems.
- The imbalance of LH is usually checked by conducting an LH test.
- There are numerous ways to promote the healthy luteinizing hormone levels in males and females.
Understanding Luteinizing Hormone (LH)
What is Luteinizing Hormone?
Luteinizing Hormone, abbreviated as LH, is medically defined as hormone that plays a crucial role in ovulation and fertility. The body’s gonadotrophin cells co-secrete FSH (follicle-stimulating hormone) and LH hormones in the pituitary gland.
Role in the endocrine system
In general, luteinizing hormone functions differ between males and females. However, they both significantly contribute to the production and maturation of numerous primordial germ cells.
a) Luteinizing hormone in males stimulates the testes to produce the testosterone hormone.
b) While in females, it has two prominent roles:
- Triggers ovulation
- Stimulates production of steroid hormones in the ovaries
Luteinizing hormone in women
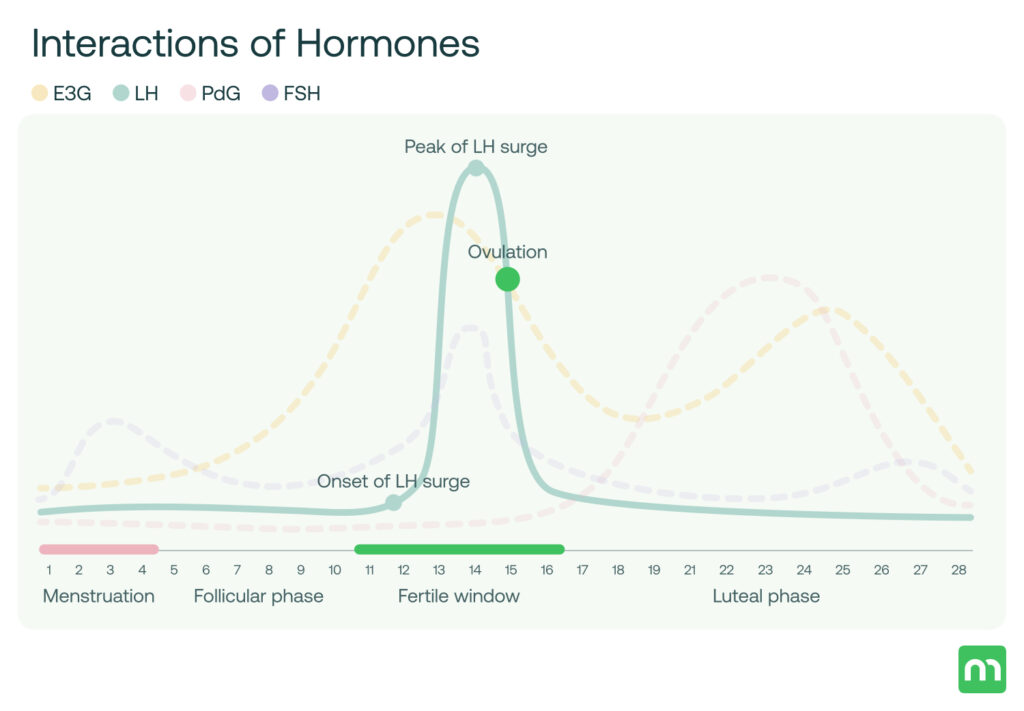
LH stimulates prime changes in women and AFAB’s (assigned female at birth) ovaries to regulate the menstrual cycle and help support pregnancy. The LH surge mainly signals the ovary to release an egg. High LH levels at this time indicate a high chance of getting pregnant.
Here’s a simple breakdown:
- LH levels surge about 24-36 hours before ovulation, setting the stage for the egg to be released into the fallopian tube.
- LH also stimulates the production of progesterone by the corpus luteum, which is important for supporting early pregnancy if the egg is fertilized.
- After ovulation, LH levels return to their basal levels before the surge.
Throughout the menstrual cycle, the luteinizing hormone stimulates the corpus luteum to secrete more progesterone hormone.
Also note that, as women age and enter the perimenopause and menopause stages, their estrogen and progesterone levels decrease, resulting in increased LH levels along with FSH.
Luteinizing hormone in men
In men and AMAB (assigned male at birth), LH primarily triggers the testes to produce and secrete testosterone. The male typically requires this hormone to produce sperm. Furthermore, testosterone is keenly responsible for more body hair, muscle mass, and a deeper voice in men.
Normal LH Levels in Different Phases of the Menstrual Cycle
In general, the levels of luteinizing hormone vary from person to person depending on individual bases. They are measured through LH tests in the standard international units per liter (IU/L).
Normal LH Levels in Women
Typically, normal LH levels in blood in females are somewhere between 5-25 IU/L.
The level ranges of luteinizing hormone in blood during various menstrual cycle phases before pregnancy are as follows:
- Early Follicular Phase Levels: 1.9 to 14.6 IU/L
This phase marks the beginning of the cycle, where LH levels are typically low.
- LH Surge/Ovulation Levels: 12.2-118.0 IU/L (peak time after your LH surge, almost the middle of menstrual cycle)
The LH surge is crucial as it triggers ovulation. Understanding its timing is key for identifying the most fertile period.
- Luteal Phase Levels: 0.7 to 12.9 IU/L (ending phase of the cycle)
- Pregnancy: <1.5 IU/L (post-ovulation phase)
Following ovulation, the luteal phase sees an increase of progesterone as the body prepares for a potential pregnancy.
In men, the standard level of luteinizing hormone (LH) typically ranges from about 1.7 to 8.6 IU/L.
Now, these are standard LH test values that indicate normal ranges. However, it’s recommended to discuss your test results with a professional. Slight changes in these normal levels, either high or low, may indicate various health issues.
How to Test Your LH Levels
LH Test
It is a medical test to measure the amount and levels of gonadotropin hormone in your blood. A doctor might ask you to conduct this test to check the following issues.
- Pituitary gland problems like fatigue, decreased appetite, or abrupt weight gain or loss
- Hormonal imbalance disturbing your regular menstrual cycle
- Certain medical conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
- Fertility problems related to ovulation, causing difficulty in becoming pregnant
- Menopause and many more.
LH Test Methods
Typically, there are three main ways of testing LH levels in females: urine tests, blood tests and saliva tests.
Urine Tests at Home
As mentioned above, LH plays a crucial role in the ovulation process. LH levels surge approximately 24-36 hours before ovulation occurs, signaling the ovary to release an egg. This surge is what most tests detect, as it’s the most reliable hormonal indicator of impending ovulation. By measuring LH levels, women can identify their most fertile days, which are just before and during this LH surge, making it easier to plan for conception or understand their menstrual cycle better.
When considering tracking ovulation, you have several options available, providing different kinds of the results.
Let’s take a look at ovulation prediction kits (OPKs) first. OPKs are available in two types: threshold-based and semi-quantitative tests. Threshold-based tests provide a simple positive or negative result, indicating whether your LH levels are above or below a predetermined standard. This approach isn’t tailored to individual variations, so if your natural LH levels differ significantly from the general population’s, these tests may not be suitable for you.
Semi-quantitative tests measure LH levels and assign a number that corresponds to low, high, or peak ranges. This enables you to monitor the pattern and fluctuations of your LH levels over time. By identifying when you reach your peak LH levels, you can accurately determine your most fertile days.
An OPK can provide a 12 to 36-hour advance notice before ovulation occurs. However, since these tests do not give exact LH level readings, they may not be effective for individuals with consistently high or low hormone levels.
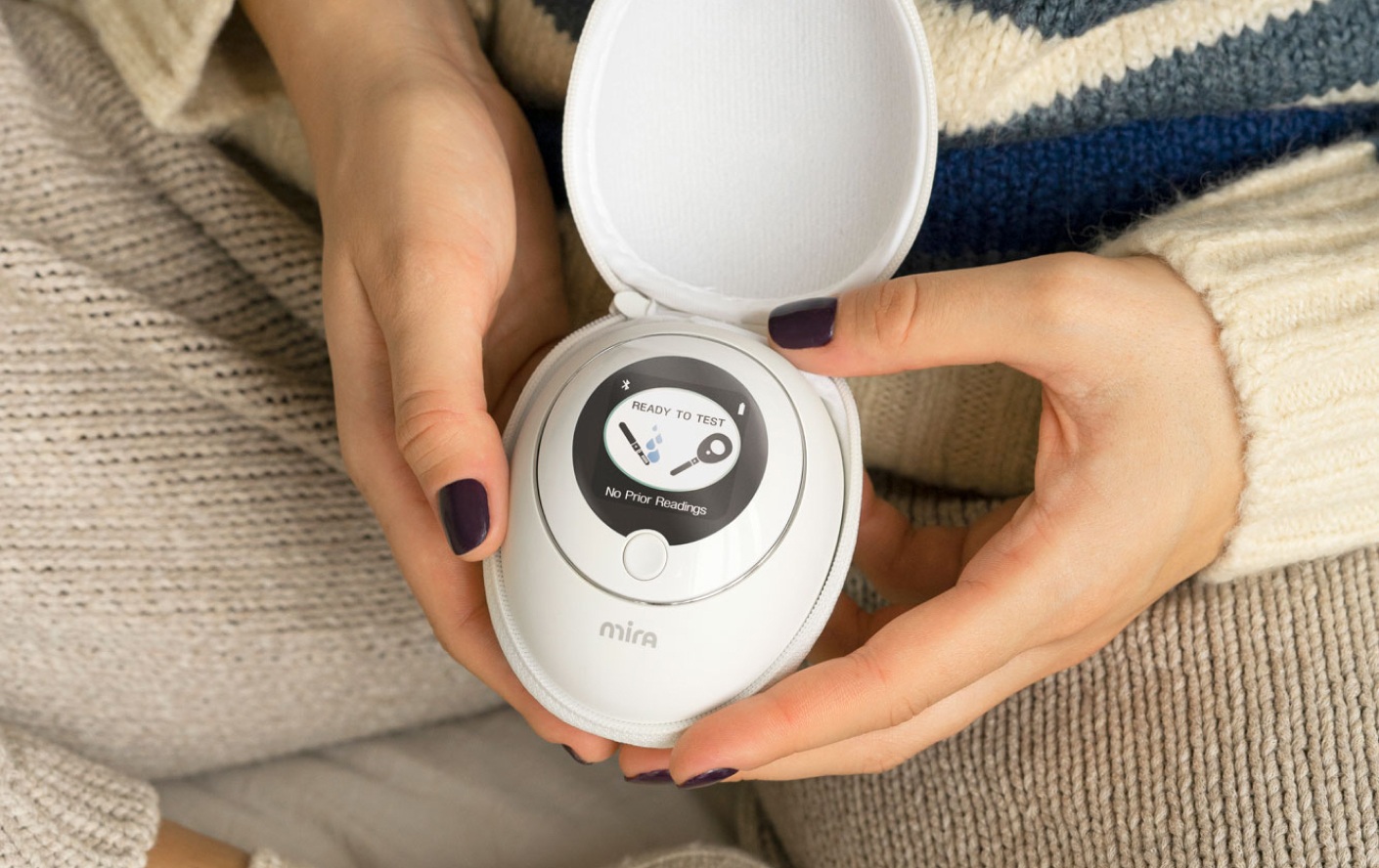
So, alternatively, for those seeking a more precise method, the Mira Hormone Monitor offers an advanced solution. Equipped with ultra-sensitive technology and backed by a powerful AI trained on over 13 million hormone data points, Mira not only tracks luteinizing hormone (LH) but also other key sex hormones, delivering ovulation prediction with 99% lab-grade accuracy. This makes it an excellent option for anyone looking to gain deeper insights into their fertility health.
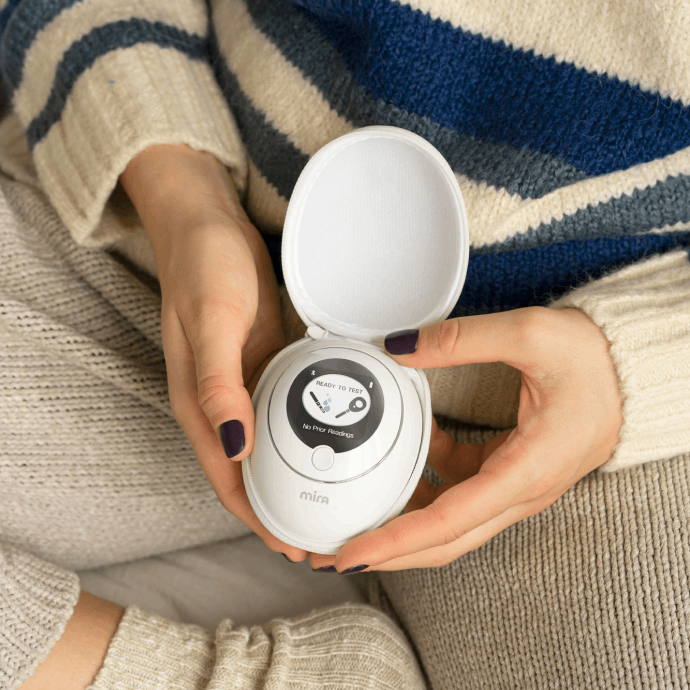

If you aren’t sure how to react upon the results, you may consult a Hormone Health Coach at Mira’s online Hormone Health Clinic for Fertility. They will offer personalized analysis of your results, providing tailored advice on lifestyle changes and supplement intake to optimize your hormone levels.
Blood Tests at a Clinic or Laboratory
Now, in addition to at-home testing, there is the option of doctoral lab testing. Instead of a urine sample, the lab’s doctors check LH levels through a blood test. Most commonly, the blood sample should be taken and tested on the second or third day of the menstrual cycle.
In this test, the lab technician takes a small blood sample by needle pricking or injecting it into your arm’s vein. The blood sample is then processed and analyzed using lab techniques to determine the levels of luteinizing hormone in the blood.
The key benefit of medical lab testing over home-based testing is getting more accurate results, while you can ask for further possible preventions, treatments, or testing by having a live detailed discussion with the doctor.
What Influences LH Levels?
Factors Affecting LH Levels
High LH factors
Typically, a few most common lifestyle and dietary factors that can elevate normal LH levels in women primarily include the following:
- Alcohol intake
- Smoking
- Nutritional deficiencies
- Excessive exercise, or lack of regular physical activity.
Low LH factors
On the other hand, the standard living and eating habits that result in low levels of luteinizing hormone in women comprise the following things:
- Metformin
- Glucocorticoids
- Cannabis
- A diet rich in soy products
- Isoflavones, and many more
Age impact on LH levels
Undoubtedly, the levels of various hormones change over time. Age is a crucial factor impacting those levels. Especially in the case of females, the hormone levels vary significantly depending upon the life stage. Normal LH levels range in females at different menstrual cycle phases is within 5 – 25 IU/L. After menopause, the range becomes higher than 25 IU/L.
Lifestyle factors: diet, exercise, and stress
Besides age, several other lifestyle factors also greatly influence the stimulation of glands and the production of various hormones in both men’s and women’s bodies. A few of those critical factors are:
- Stress or anxiety
- Eating habits
- Exercise routine
- Alcohol or tobacco consumption
- Lack of proper sleep
- An inactive lifestyle, etc.
Common health conditions affecting LH levels: PCOS, menopause
Hormonal contraception can disturb the average production of LH hormone. Primary ovarian insufficiency (POI) may also disturb LH levels in women.
High or low levels of LH hormones indicate abnormal health implications.
- High LH Levels: In women, an increase in LH levels may be caused by conditions like PCOS, premature ovarian failure, or menopause. In men, high LH levels may show primary testicular failure.
- Low LH Levels: Decreased LH levels cause irregular menstrual cycles, infertility, or absence of periods in women. In men, low LH levels may indicate low testosterone, less interest in sexual activity, and impotence. Causes of low levels: pituitary gland disorders, malnutrition, underweight, excessive stress.
Interpreting LH Test Levels: When to Be Concerned
Symptoms of Abnormal LH levels
As mentioned, there are standard LH levels for both men and women. If, upon testing, your results go out of these normal ranges, your luteinizing hormone levels are abnormal. Below are some symptoms and underlying health conditions associated with low and high LH abnormalities.
Low LH Levels Symptoms
- Irregular or missing periods
- Delayed puberty
- Fatigue and tiredness all the time
- Decreased pubic hair
- Excessive hair loss
- Complex breast milk production
- Difficulty getting pregnant
Low luteinizing hormone levels signify that the individual’s pituitary gland is malfunctioning. Typically, some underlying conditions, associated with low LH levels, are functional hypothalamic amenorrhea that occurs when a female misses or has irregular periods, mainly due to excessive or rigorous exercise and Kallman syndrome that leads to insufficient estrogen, testosterone and progesterone production.
High LH Levels Symptoms
- Skipped or no periods
- Change in sex drive
- Vaginal dryness
- Frequent mood swings
- Shorter or longer menstrual cycle
- Stubborn weight loss or gain
- Difficulty becoming pregnant
High LH levels in the blood hint that a person’s sexual organs are not secreting the required levels of steroids essential for the reproductive process. And a high LH level is linked to PCOS, a condition leading to various symptoms such as irregular periods, difficulty getting pregnant, and acne, facial and body hair growth. It is also common for Turner syndrome and Klinefelter syndrome – two widespread genetic conditions affecting DMAB individuals.
Treatment Options
The most common treatment options:
- Hormonal therapy
- Injections of Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone (GnRH) agonist and antagonists
Natural remedies can be a supportive approach for managing LH imbalances. Here are some commonly considered natural options.
Supplements: They can help regulate hormonal imbalances by affecting the pituitary gland, which controls the production of LH and other hormones.
Dietary Changes: A balanced diet rich in whole foods, fiber, and lean proteins can help manage insulin levels, which are closely linked to hormone production. Reducing intake of processed foods and sugars is often recommended. Including nuts, seeds, and dairy products, which are high in minerals and vitamins, along with fruits and vegetables loaded with antioxidants, helps maintain hormone balance.
Exercise: Regular physical activity can help balance hormones by improving insulin sensitivity and reducing stress.
Herbal Teas: Certain herbal teas, such as spearmint, might help lower LH levels and balance hormones when consumed regularly.
If you still need help with understanding LH levels, you can contact Mira’s health coaches at any time from the comfort of your home. They will suggest the best treatment options based on your bodily needs and condition.
Conclusion
The luteinizing hormone is one of the two main gonadotrophin hormones. These induce reproductive maturation, and fertility in women and men. Typically, natural LH production and secretion consistently increase until puberty. Later, homeostasis continues throughout adulthood until the menopause stage is reached.
Factors such as age, health conditions, and even the standards used by different laboratories can affect what is considered a typical LH range. Monitoring these levels is essential, particularly for diagnosing and managing reproductive issues. Even a slight rise or fall may disturb the hormonal balance, resulting in difficulty in pregnancy or complete infertility.
Adopting a healthy lifestyle can also influence LH levels and overall hormonal balance. A diet rich in nutrients, regular exercise, and managing stress effectively can all contribute to maintaining stable hormone levels. Professional healthcare providers can offer personalized guidance and treatment options to help ensure optimal hormonal health.
Mira’s Editorial Process
All content produced by Mira meets stringent editorial standards, ensuring excellence and accuracy in language and medical precision. Every piece undergoes thorough fact-checking and review by qualified professionals. Check out our full editorial process to learn more.